CUT
Cut doesn't refer to the shape of the diamond. Cut refers to how a diamond's facets are cut. This determines how light is returned to the top of the stone. Ultimately, it is responsible for how “sparkly” a diamond is – its brilliance, fire, and scintillation.
Brilliance is the combination of all of the white light reflected from the surface and the inside of the diamond.
Fire are flashes of color you see in a polished diamond
Scintillation are flashes of light you see when the diamond, the light, or the observer moves.
For the best results, proportions of its facets, symmetry, the relationship of its weight to its diameter, girdle thickness, and quality of its polish have to come together in just the right way.
An ideal cut diamond offers the most brilliance, fire and scintillation.
COLOR
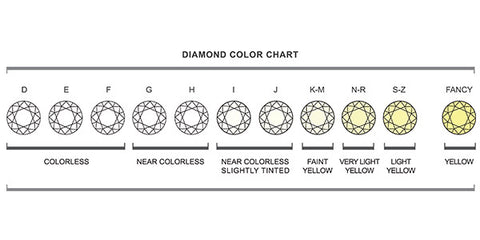
Color is measured using the GIA® (Gemological Institute of America) D-to-Z diamond color grading system. This system is the most widely accepted for grading. All diamonds are evaluated based on the absence of color.
This lack of color is measured in degrees based on comparisons with masterstones, made while viewing under controlled lighting and conditions. These color distinctions are invisible to the untrained eye and should be left to a trained diamond grader.
This scale illustrates the range of diamond color:
CLARITY
The clarity of a diamond refers to the number and location of inclusions and blemishes. These imperfections can be internal or on the surface. An imperfection can interfere with the reflection of light within the stone, therefore can hinder the brilliance of the diamond.
Internal characteristics = Inclusions
External characteristics = blemishes
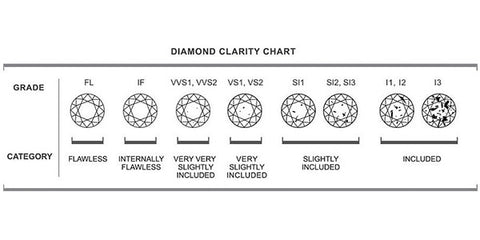
This chart shows how a diamond’s clarity is graded:
|
FL, IF |
Flawless: No internal or external flaws |
|
VVS1, VVS2 |
Very, very slightly included: Very difficult to see inclusions under 10X magnification |
|
VS1, VS2 |
Very, slightly included: Inclusions are not typically visible to the unaided eye |
|
SI1, SI2 |
Slightly included: Inclusions are visible under 10X magnification and may be visible with the unaided eye |
|
I1, I2, I3 |
Included: Inclusions are visible with the unaided eye |
CARAT
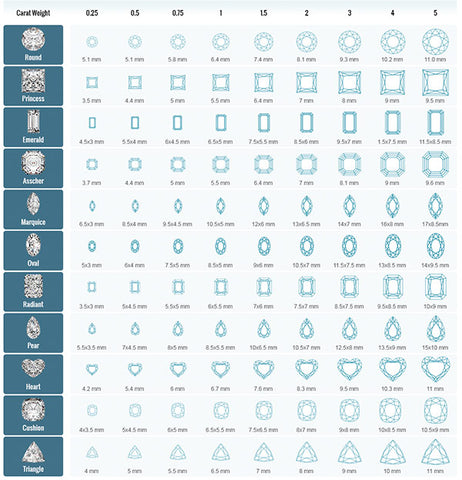
Carat weight relates to the size of a diamond. The weight of a diamond is expressed in carats. Carat directly correlates to the price of the diamond. This happens because the supply is low (larger = rarer) and demand is high (larger = more popular).
1 Carat = 200 milligrams
1 Point = 0.01 carat = 1/100 of a carat (a 1.0 carat diamond = 100 points)
Diamonds of equal weight are not necessarily the same size. Different proportions and depths will result in different size and weight combinations.
Our prices, craftsmanship, service, and expertise are hard to beat when comparing everything equally.
